|
|
| Night vision devices gather
existing ambient light (starlight, moonlight or infra-red light)
through the front lens. This light, which is made up of photons
goes into a photocathode tube that changes the photons to
electrons. The electrons are then amplified to a much greater
number through an electrical and chemical process. The electrons
are then hurled against a phosphorus screen that changes the
amplified electrons back into visible light that you see through
the eyepiece. The image will now be a clear green-hued amplified
re-creation of the scene you were observing. |
|
To Learn More About The Different
Types Of Night Vision Products "click"
Night Vision
Products
|
| A Night Vision Device can be
either a 1st, 2nd, 3rd or 4th generation unit. What this stands
for is what type of light intensifier tube is used for that
particular device The light intensifier tube is the heart and
soul of an NVD. |

1st generation is currently the most popular type of
night vision in the world. Utilizing the basic principles
described earlier, a 1st generation will amplify the existing
light several thousand times letting you clearly see in the
dark. These units provide a bright and sharp image at a low
cost, which is perfect, whether you are boating, observing
wildlife, or providing security for your home. You may notice
the following when you are looking through a 1st gen unit
- A slight high-pitched whine when the unit is on.
- The image you see may be slightly blurry around the edges.
This is known as Geometric Distortion.
- When you turn a 1st gen off it may glow green for some
time.
- These are inherent characteristics of a 1st gen and are
normal.
|
|
|

2nd generation is primarily used by law enforcement or
for professional applications. This is because the cost of a 2nd
gen unit is approximately $500.00 to $1000.00 more then a 1st
gen. The main difference between a 1st and a 2nd generation unit
is the addition of a micro-channel plate, commonly referred to
as a MCP. The MCP works as an electron amplifier and is placed
directly behind the photocathode. The MCP consists of millions
of short parallel glass tubes. When the electrons pass through
these short tubes, thousands more electrons are released. This
extra process allows 2nd generation units to amplify the light
many more times then 1st generation giving you a brighter and
sharper image. |
|
|

3rd generation By adding a sensitive chemical, gallium
arsenide to the photocathode a brighter and sharper image was
achieved over 2nd generation. An ion barrier film was also added
to increase tube life. Gen. 3 provides the user with good to
excellent low light performance. |
|
|

4th Generation / Gated Filmless tubes:
4th generation / Gated Filmless technology represents the
biggest technological breakthrough in image intensification of
the past 10 years. By removing the ion barrier film and "Gating"
the system Gen 4 demonstrates substantial increases in target
detection range and resolution, particularly at extremely low
light levels. |
The use of filmless technology and auto-gated
power supply in 4th generation image intensifiers result in:
- Up to 100% improvement in photoresponse.
- Superb performance in extremely low light level (better
S/N and EBI)
- At least triple high light level resolution (a minimum of
36 lp/mm compared to 12 lp/mm)
|
|
|
| With significant improvement in contrast level
and in performance under all light conditions, 4th generation
represents the top of the line performance in the night vision
market. Note: The term 4th generation is used/accepted among
Night Vision manufactures to describe gated filmless tubes.
However, this designation is widely debated and is currently
referred to as Filmless & Gated image intensifiers by the US
Military. |
 |
 |
|
Gen 4 technology improves night operational effectiveness
for military users of night vision goggles and other night
vision devices. The filmless MCP provides a higher
signal-to-noise ratio than Gen 3, resulting in better image
quality (less scintillation) under low-light conditions. The
gated power supply further improves image resolution under
high light conditions, and the reduced halo minimizes
interference from bright light sources. These improvements
also substantially increase the detection range of the
systems. |
|
|
|
 |
Gen 3
Omni IV |
Gen 4 |
%
Improvement |
| Photoresponse (µA/Im) |
1800 |
1800 |
- |
| Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
21.0 |
25.0(ground) |
20% Higher |
| 26.0(air) |
24% Higher |
| Resolution(lp/mm) |
64 |
64 |
- |
| Halo(mm) |
1.25 |
0.75 |
40% smaller |
| Reliability(hours) |
10,000 |
10,000 |
- |
|
|
|
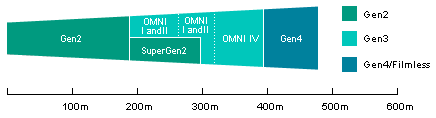
RANGE IMPROVEMENT
|
| Relative direction ranges |
| PVS-7 System |
| Overcast Starlight Conditions (-1x10E-5 tc) |
| Vehicle Size Target, 30% Contrast |
 |
|
|
|
 |
Gen 2 |
SuperGen 2 |
Gen 3 OMNI
I and II |
Gen 3 OMNI
III |
Gen 3 OMNI
IV |
Gen IV |
| Detection Range (m) |
170 |
270 |
240 |
290 |
360 |
430 |
% Improvement
over Gen II |
0% |
60% |
40% |
70% |
110% |
153% |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
 All
Starlight scopes need some light to amplify. This means that if
you were in complete darkness you could not see. Due to this we
have a built in infra-red illuminator (IRI) on all of our
scopes. Basically what an IRI does is throw out a beam of
infra-red light that is near invisible to the naked eye but your
NVD can see it. This allows you to use your scope even in total
darkness. The IRI works like a flashlight and the distance you
can see with it will be limited. We do use the most powerful
eye-safe illuminator on the market. This allows our IRI to
extend out to 100 yards However, because of the power at a short
distance the IRI may cover only 40-60% of the viewing area. All
Starlight scopes need some light to amplify. This means that if
you were in complete darkness you could not see. Due to this we
have a built in infra-red illuminator (IRI) on all of our
scopes. Basically what an IRI does is throw out a beam of
infra-red light that is near invisible to the naked eye but your
NVD can see it. This allows you to use your scope even in total
darkness. The IRI works like a flashlight and the distance you
can see with it will be limited. We do use the most powerful
eye-safe illuminator on the market. This allows our IRI to
extend out to 100 yards However, because of the power at a short
distance the IRI may cover only 40-60% of the viewing area. |
|
|
|
|
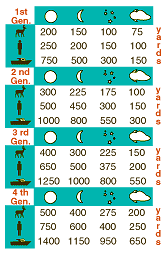 There are many different variables that can effect the distance
that you can see with a Night Vision device. First, what are you
trying to see? Are you looking for another boat on the water or
are you looking for a rabbit in the woods? The larger the object
the easier it is too see. Plus, are you trying to see details
(what we call recognition range) or are you just trying to see
if something is there or maybe you will just see movement but
won't be able to 100% determine who or what it is. This is
called detection range. Second. Another variable is lighting
conditions. The more ambient light you have (starlight,
moonlight, infrared light) the better and further you will be
able to see You can always see further on a night where the moon
and stars are out then if it is cloudy and overcast. We
typically state that you can tell the difference between a male
and a female or a dog and a deer at about 75 to 100 yards.
However, if you were looking across an open field and there was
a half moon out you could see a barn or a house 500 yards away.
There are many different variables that can effect the distance
that you can see with a Night Vision device. First, what are you
trying to see? Are you looking for another boat on the water or
are you looking for a rabbit in the woods? The larger the object
the easier it is too see. Plus, are you trying to see details
(what we call recognition range) or are you just trying to see
if something is there or maybe you will just see movement but
won't be able to 100% determine who or what it is. This is
called detection range. Second. Another variable is lighting
conditions. The more ambient light you have (starlight,
moonlight, infrared light) the better and further you will be
able to see You can always see further on a night where the moon
and stars are out then if it is cloudy and overcast. We
typically state that you can tell the difference between a male
and a female or a dog and a deer at about 75 to 100 yards.
However, if you were looking across an open field and there was
a half moon out you could see a barn or a house 500 yards away.
Remember, that the purpose of an NVD is to see in the dark not
necessarily a long ways like a binocular. |
|
|
|
|
 As
you look through a night vision device you may notice black
spots on the screen. A NVD is similar to a television screen and
attracts dust and dirt. Typically these spots can be cleaned.
However, this may also be a spot in the tube itself. This is
normal. Most tubes will have some spots in them. These black
spots will not affect the performance or reliability of the
night vision device. As
you look through a night vision device you may notice black
spots on the screen. A NVD is similar to a television screen and
attracts dust and dirt. Typically these spots can be cleaned.
However, this may also be a spot in the tube itself. This is
normal. Most tubes will have some spots in them. These black
spots will not affect the performance or reliability of the
night vision device. |
|
Offering The Following Night Vision
Products:
Night Vision Rifle Scopes
Night Vision Goggles
Night Vision Binoculars
Night Vision Monoculars
Day/Night Systems
Multipurpose Night Vision Systems
[Night
Vision Not For Export !]
Also Offering The Following Products!
[HOME]
Rifle & Handgun Scopes
Binoculars
Spotting Scopes Laser
Rangefinders
Rings
& Bases
How To Order

Telephone & Mail Order Hours: Mon. - Fri.
7:00 AM - 6:00 PM Pacific Time
Saturdays 8:00 A.M. - 2:00 P.M., Closed Sundays
Telephone - Orders - 1-(800) 641-4470
All Other Questions & Outside The USA 1-(925) 825-9803
Fax Orders 1 (925)
825-9027
Show Room Open Monday - Friday
& 1/2 Day On Saturday
Questions, UPS Tracking and e-mail:
Info@BearBasin.com
To Subscribe to Our Newsletter and
e-mail Specials, Send Us a Note At: Newsletter@BearBasin.com
|









 All
Starlight scopes need some light to amplify. This means that if
you were in complete darkness you could not see. Due to this we
have a built in infra-red illuminator (IRI) on all of our
scopes. Basically what an IRI does is throw out a beam of
infra-red light that is near invisible to the naked eye but your
NVD can see it. This allows you to use your scope even in total
darkness. The IRI works like a flashlight and the distance you
can see with it will be limited. We do use the most powerful
eye-safe illuminator on the market. This allows our IRI to
extend out to 100 yards However, because of the power at a short
distance the IRI may cover only 40-60% of the viewing area.
All
Starlight scopes need some light to amplify. This means that if
you were in complete darkness you could not see. Due to this we
have a built in infra-red illuminator (IRI) on all of our
scopes. Basically what an IRI does is throw out a beam of
infra-red light that is near invisible to the naked eye but your
NVD can see it. This allows you to use your scope even in total
darkness. The IRI works like a flashlight and the distance you
can see with it will be limited. We do use the most powerful
eye-safe illuminator on the market. This allows our IRI to
extend out to 100 yards However, because of the power at a short
distance the IRI may cover only 40-60% of the viewing area.  There are many different variables that can effect the distance
that you can see with a Night Vision device. First, what are you
trying to see? Are you looking for another boat on the water or
are you looking for a rabbit in the woods? The larger the object
the easier it is too see. Plus, are you trying to see details
(what we call recognition range) or are you just trying to see
if something is there or maybe you will just see movement but
won't be able to 100% determine who or what it is. This is
called detection range. Second. Another variable is lighting
conditions. The more ambient light you have (starlight,
moonlight, infrared light) the better and further you will be
able to see You can always see further on a night where the moon
and stars are out then if it is cloudy and overcast. We
typically state that you can tell the difference between a male
and a female or a dog and a deer at about 75 to 100 yards.
However, if you were looking across an open field and there was
a half moon out you could see a barn or a house 500 yards away.
There are many different variables that can effect the distance
that you can see with a Night Vision device. First, what are you
trying to see? Are you looking for another boat on the water or
are you looking for a rabbit in the woods? The larger the object
the easier it is too see. Plus, are you trying to see details
(what we call recognition range) or are you just trying to see
if something is there or maybe you will just see movement but
won't be able to 100% determine who or what it is. This is
called detection range. Second. Another variable is lighting
conditions. The more ambient light you have (starlight,
moonlight, infrared light) the better and further you will be
able to see You can always see further on a night where the moon
and stars are out then if it is cloudy and overcast. We
typically state that you can tell the difference between a male
and a female or a dog and a deer at about 75 to 100 yards.
However, if you were looking across an open field and there was
a half moon out you could see a barn or a house 500 yards away.
 As
you look through a night vision device you may notice black
spots on the screen. A NVD is similar to a television screen and
attracts dust and dirt. Typically these spots can be cleaned.
However, this may also be a spot in the tube itself. This is
normal. Most tubes will have some spots in them. These black
spots will not affect the performance or reliability of the
night vision device.
As
you look through a night vision device you may notice black
spots on the screen. A NVD is similar to a television screen and
attracts dust and dirt. Typically these spots can be cleaned.
However, this may also be a spot in the tube itself. This is
normal. Most tubes will have some spots in them. These black
spots will not affect the performance or reliability of the
night vision device. 